

As a result of 23.5° Earth’s axial tilt, either the Southern or Northern Hemisphere acquires the extreme intensity of the sun’s rays. It moreover depicts the symbolic demise and rebirth of the sun.ĭuring the June solstice, sun declination is about 23.5°N, and the December solstice is 23.5°S. Throughout history, the winter solstice in many cultures has been a significant time of the year. At the solstice time, one can say that the sun is standing. Likewise, in December, the sun reaches its highest position in the sky for any observer on the south pole this day is known as the December solstice day. Solstices are called ‘June Solstice’ or ‘December Solstice.’ In June, the sun reaches its highest position in the sky for any observer on the North pole this day is known as June solstice day. Winter solstice- The day of the solstice has the least amount of sunlight of the year in either of the hemispheres except the equator. Summer solstice- The day of the solstice is either of the hemispheres which have the most sunlight of the year. At poles, the solstice is a maximum of radical exposure to sunlight, while at the Equator, solstices are hardly noted at all. Earth’s latitude acquaintance solstice in varied ways. In several countries, the seasons are specified by the citation to the solstice and the equinoxes. One on the 21st of June and the second on the 21st of December. The word solstice is derived from the Latin language. SolsticeĪn event that happens when the sun seems to reach its most northerly or southerly expedition relative to the celestial equinoctial line on the celestial sphere is known as a solstice. These effects can last for a duration varying between a few minutes to an hour. One prominent effect of an equinox is that on days falling around an equinox, the sun is directly behind the earth and hence the high energy leads to disabling and an overload on the reception circuits of geostationary satellites. This implies that equinox is that time of the year when the rays of the sun fall directly on the equatorial plane.

This is also why during an equinox the sun appears to rise at one rotational pole of the Earth and appears to set for an observer at the opposite rotational pole. The equinoxes are that time of the year when an equal amount of sunlight illuminates both the hemispheres of the earth.
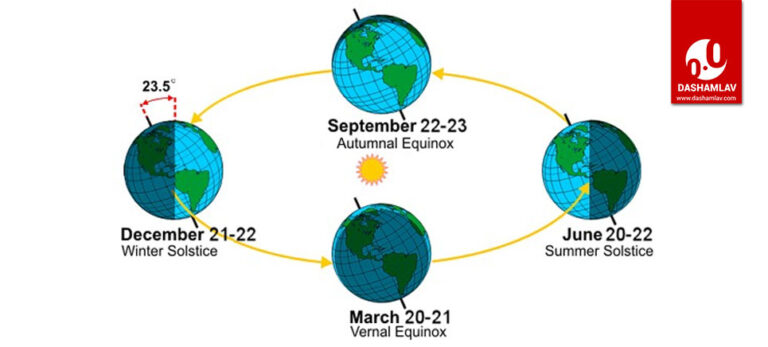
The southward equinox marks the beginning of autumn. The northward equinox marks the beginning of spring in most regions and is celebrated as the new year per the Hindu, Persian, and Iranian calendars. As the name suggests, a Northward equinox would mean that the Celestial equator is being crossed by the solar declination in the northward direction and vice versa. Ignoring the hemispheres, the general names of both the equinoxes are Northward equinox and southward equinox, respectively. The date of an equinox may vary due to various factors, including the leap year. The reverse is true in the case of the southern hemisphere. In the Northern hemisphere, the Equinox of March is the vernal equinox, while the Equinox of September is called the Autumnal equinox. An equinox occurs because the plane of the earth’s equator passes directly from the centre of the sun’s geometric plane, which means that the centre of the visible portion of the sun is falling directly over the equator. This event takes place two times a year, i.e., on 20 March and 23 September. EquinoxĮquinox is that time of the year when the daytime and the nighttime are equal. Before looking at the differences between Equinox and solstice, let us look in detail at the equinox and solstice and what happens during that time. Solstice is when people on earth experience long days and nights. Equinox is when the length of day and night are the same. Equinox and Solstices, are two reasons why the earth has different seasons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
